
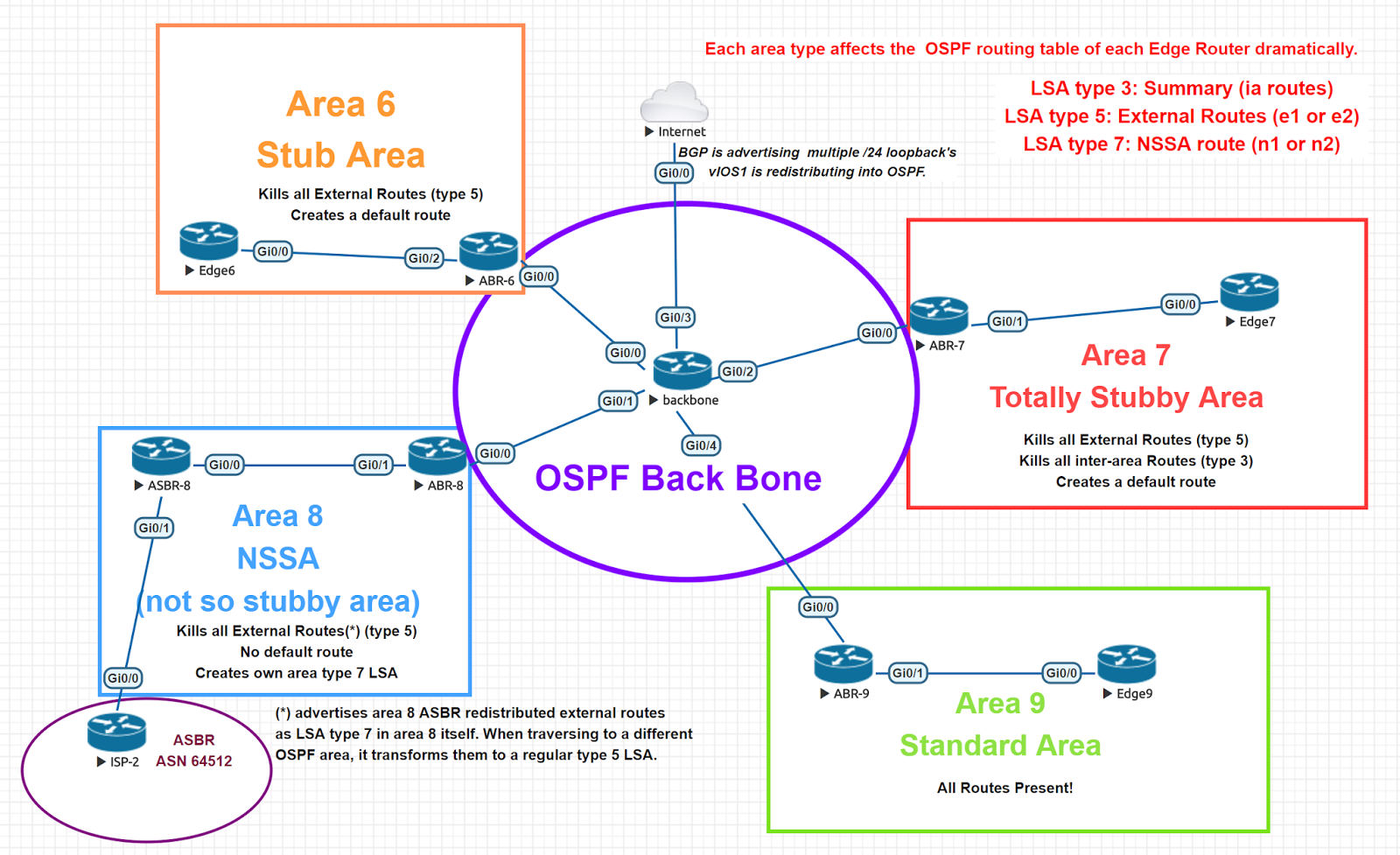
Type 5: Created by the ASBR, this type describes external interconnections to the Autonomous System (AS).

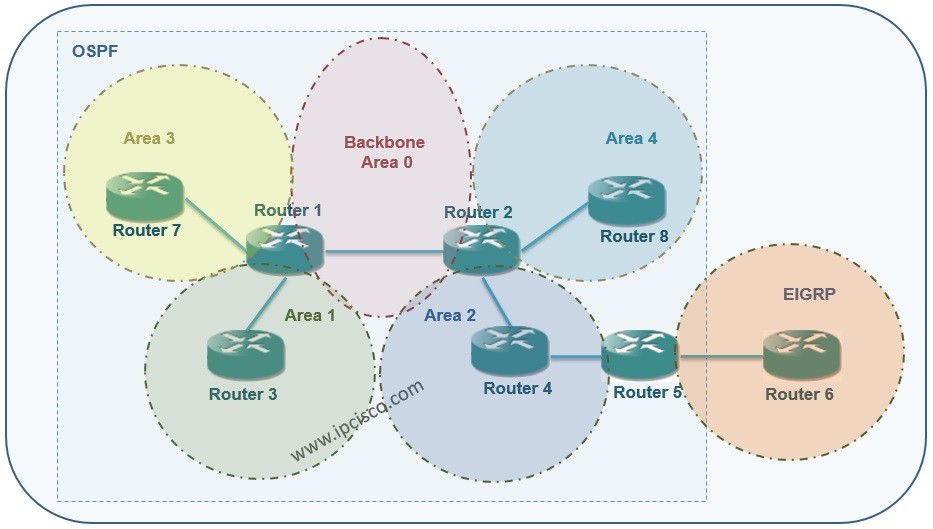
Type 3 is also the “default-information-originate.” Routes to the ASBR are classified as Type 4 routes (interarea summary route). Type 3 describes network pathways and is used to summarise data. Type 3/4: ABR-generated summary link advertising describing inter-area routes. In the output of the “show ip route” command, these routes are marked as O IA. The term “OSPF Inter-Area route” refers to a route that crosses an OSPF Area Border Router (ABR). Thousands of people flocked to the area where the network is located (intra-area route). Type 2: Network link advertising are advertising published by specified routers that describe the set of routers connected to a specific network. In the output of the “show ip route” command, these routes are marked flagged as O. Routes that originate within an area are known as Intra-Area routes by routers in the same area in a multi-area OSPF network. Only a single region was flooded (intra-area route). Type 1: Advertisements for router links created by each router for each area to which it belongs. Because BRs do not have an interface to the other OSPF regions, they would be considered ABRs if they did. 4.Backbone Routersīackbone routers are routers with interfaces that exclusively connect to the backbone area (BRs). The redistribute static or redistribute connected commands within the OSPF routing process is one approach to configure or activate an ASBR in OSPF. BGP can also be used to connect several autonomous systems. The redistribution command is frequently used on Cisco routers to connect two routing protocols. ASBRs must be located in an OSPF area that is not stubbed. OSPF and other routing protocols, such as RIP or BGP, are both used by ASBRs. Every router in an AS understands how to reach each ASBR using its AS. The transferred external routing information is advertised by ASBRs throughout their AS. 3.Autonomous Systems Boundary RoutersĪSBRs are connected to many ASs and communicate with routers in other ASs to exchange routing information. Also, when OSPF reroutes traffic from other routing protocols, such as static routes, a router becomes an ASBR, and it can exist in a pure OSPF network. Routing information is redistributed between networks using this protocol. Between an OSPF autonomous system and a non-OSPF network is a router. 2.Area Borders Routersīecause ABRs are linked to various OSPF areas, a network can have several ABRs. Because they belong to only one area, these routers have a single link-state database. Internal routers are routers that belong to the same OSPF region as their directly connected networks. 1.Routers for internal use: Internal routers


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
